Postgres SQL
From Blue-IT.org Wiki
Contents
[hide]General
This guide is tested on ubuntu feisty with postgresql 8.2. It should work for former and future versions of both too.
General documentation you will find here:
You should read this in advance to make shure the concepts behind postgresql configuration, startup and security (e.g. 'roles).
User Management
General Dokumentation
- (GERMAN) Postgres on Selflinux.org
- (GERMAN) German Postgres Page
Ubuntu Feisty, Gutsy
- Thanks to the article on hocuspok.us, it was very easy to set up postgresql-8.2 running on ubuntu.
- Another Quicklink for ubuntu: PostgreSQL Quickstart
Installation
Install postgresql
sudo apt-get install postgresql-8.2 postgresql-client-8.2
For administration we install pgadmin3
sudo apt-get install pgadmin3 pgadmin3-data
Set database admin account
Alter the password for the standard postgres user account (as root)
sudo su postgres -c psql template1
Inside the database:
template1=# ALTER USER postgres WITH PASSWORD 'new_password'; template1=# \q
/etc/postgresql/8.2/main/postgresql.conf
Assure that the server is accessible on localhost
sudo gedit /etc/postgresql/8.2/main/postgresql.conf
listen_addresses = 'localhost' password_encryption = on
/etc/postgresql/8.2/main/pg_hba.conf
Security and server settings. If you like to use the server in a network you have to pay attention to three points:
- Add the server ip to the listen adress
- Allow special clients to connect
- Think about using ssl, if you connect through the internet
sudo gedit /etc/postgresql/8.2/main/pg_hba.conf
# - Connection Settings - # what IP address(es) to listen on; # comma-separated list of addresses; listen_addresses = 'localhost,server_IP' # Allow any user on the local system to connect to any database under # any user name using Unix-domain sockets (the default for local # connections). # # Database administrative login by UNIX sockets local all all trust # TYPE DATABASE USER CIDR-ADDRESS METHOD # "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only local all all md5 # IPv4 local connections: host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5 # IPv6 local connections: host all all ::1/128 md5 # Connections for all PCs on the subnet # # TYPE DATABASE USER IP-ADDRESS IP-MASK METHOD # e.g. host all all 192.168.0.0/24 md5 # e.g. host all all 192.168.0.10 255.255.255.0 md5 host all all [ip address] [subnet mask] md5
Restart postgresql
sudo /etc/init.d/postgresql-8.2 restart
SuSE 10.1, 10.3
First I have to mention that it is almost impossible to get a howto to install postgresql on SuSE. I really don't now why. Finding an according howto for ubuntu was a matter of minutes. Not even a search at support database of SuSE got ANY result. This is really poor.
Installation
Prior 10.3
- Via YaST and the previously mentioned packman repository
Administration
Pgadmin III
You will find them in the guru repositories:
- prior to opensuse 10.3
- via YaST and the previously mentioned packman repository
- opensuse 10.3 and later
- Download the rpm package from the pgadmin site: Direct from pgadmin.org or pgadmin 10.3
Post Installation
Start the server for the first time:
rcpostgresql start
Login
su postgres -c psql postgres postgres=#
Configuration files
- all configuration files are in
cd /usr/share/postgresql
You have to copy the /usr/share/postgresql/*.sample files to .conf and edit them according to your needs.
cp pg_hba.conf.sample pg_hba.conf cp postgresql.conf.sample postgresql.conf
I edited the pg_hba.conf (the security settings) according to a debian/ubuntu setup. Delete everything in the original file and put in this content:
# Database administrative login by UNIX sockets local all postgres ident sameuser # TYPE DATABASE USER CIDR-ADDRESS METHOD # "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only local all all ident sameuser # IPv4 local connections: host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5 # IPv6 local connections: host all all ::1/128 md5 # Allow Connections for certain PCs on a subnet. # Alter this according to your own hosts/network configuration. # # TYPE DATABASE USER IP-ADDRESS IP-MASK METHOD host all all 192.168.0.200 255.255.255.0 md5 host all all 192.168.0.201 255.255.255.0 md5 host all all 192.168.0.203 255.255.255.0 md5
For the postgres server settings file postgresql.conf alter the file according to the following settings:
[...] data_directory = '/usr/share/postgresql/' hba_file = 'ConfigDir/pg_hba.conf' ident_file = 'ConfigDir/pg_ident.conf' listen_addresses = 'localhost,192.168.0.1' # CHANGE TO YOUR IP port = 5432 max_connections = 100 ssl = on password_encryption = on shared_buffers = 24MB stats_row_level = on autovacuum = on default_transaction_read_only = off datestyle = 'iso, dmy' lc_messages = 'de_DE.UTF-8' lc_monetary = 'de_DE.UTF-8' lc_numeric = 'de_DE.UTF-8' lc_time = 'de_DE.UTF-8'
Administration with Pgadmin III
Pgadmin helps you with almost all administration tasks to manage your postgresql databases. From managing user accounts (roles), creating tables, schemes, constraints (e.g. primary keys) to an extended sql editor.
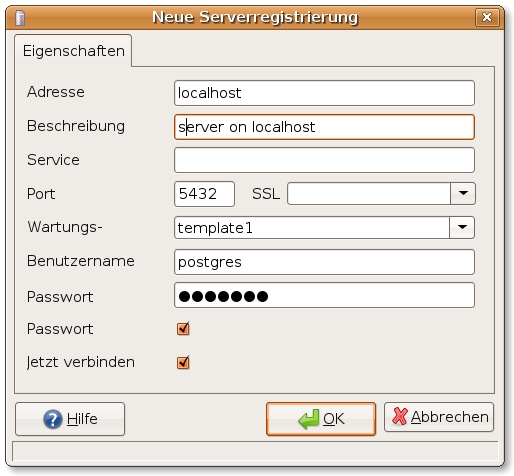
Initial registration with pgAdminIII
To be able to manage your database with pgadmin you have to configure it for the specific server:
Queries with pgadminIII
A very good tool for working with the database is the integrated sql query editor of pgadmin. Select the database you want to work with, then you can choose the query tool from the menu.
PostgreSQL queries are case sensitive. So if you specified Uppercase names for columns you have to use them exactly and in quotes. It might be necessary to add the schemata name postfixed by a dot to get a proper query:
select "Prename" from myscheme."Client";
Press <F5> to start the query.
You can easily save the queries in a file for later reuse.
Backup and restore with pgadminIII
PgadminIII makes it easy to backup your database withor without all the data. Just highlite the database you like to backup and choose the backup option from the main menu.
ODBC, Postgres and Openoffice
According to PostgreSQL-Datenbanken in OpenOffice.org 2.0 unter Linux.
Ubuntu Gutsy (7.10)
Openoffice <-> ODBC
For connection between openoffice and odebc:
apt-cache search odbc | grep unix unixodbc - ODBC tools libraries unixodbc-bin - Graphical tools for ODBC management and browsing apt-get install unixodbc unixodbc-bin
With the command ODBCConfig you can manage the configuration files (part of the package unixodbc-bin). Start it as superuser with gksu or use it to manage your local database configuration files - stored in your home directory.
But for nowe, we will - later - edit the configuration files by ourself.
ODBC <-> Postgresql
For connection between the odbc layer and the database:
apt-cache search odbc odbc-postgresql - ODBC driver for PostgreSQL apt-get install odbc-postgresql
Configuration files
Ubuntu installs its odbc libraries in /usr/lib/odbc. There are two versions of the postgres odbc driver: an ascii version (psqlodbca.so) and a unicode version (psqlodbcw.so). We are using the latter.
vim /etc/odbcinst.ini
[PostgreSQL] Description = PostgreSQL ODBC Driver Driver = /usr/lib/odbc/psqlodbcw.so Setup = /usr/lib/odbc/libodbcpsqlS.so
For system wide database location you have to edit the /etc/odbc.ini file.
There is a section Driver. You have to insert exactly the same name as defined in the odbcinst.ini between the braces, e.g. use PostgreSQL, if your odbcinst.ini is defined as [PostgreSQL]:
vim /etc/odbc.ini
[pgTestDBSource] Description = PostgreSQL Test Database Driver = PostgreSQL Servername = localhost Database = pgtest Port = 5432 ReadOnly = No
Establish connection
If you like to connect to an database via openoffice you should use a string like:
odbc://servername/databasename
Don't forget to allow connections in /etc/postgresql/8.2/main/pg_hba.conf (see above) to your database server!
The rest is really self explanatory within the openoffice database assistant ;)